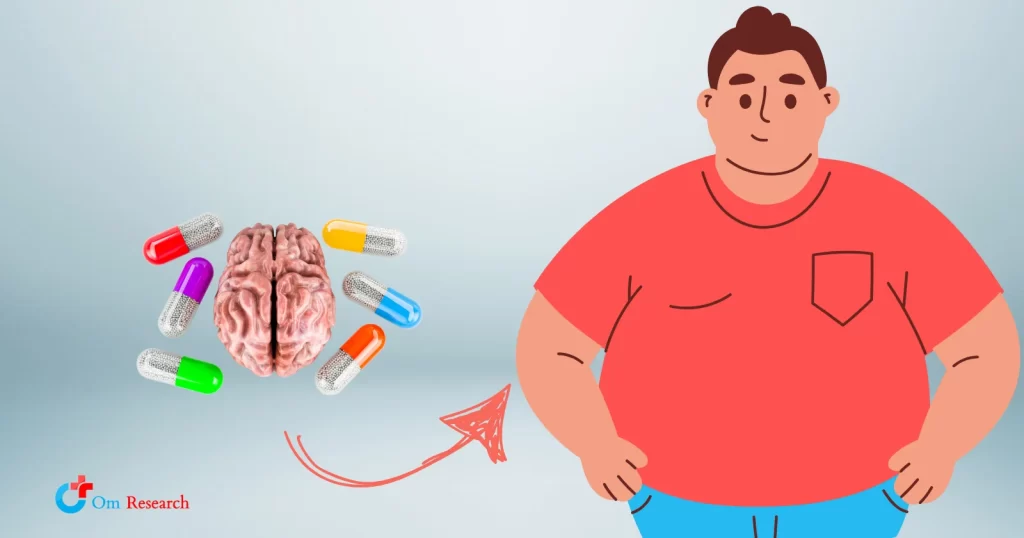
Weight gain is a common concern for adolescents taking antipsychotic medications. These medications can lead to significant weight changes, impacting physical health and self-esteem. It is essential to recognize the reasons behind this weight gain and the steps that can be taken to manage it effectively.
Understanding how antipsychotics affect metabolism, and appetite can help both parents and healthcare providers better support adolescents. Strategies for monitoring weight and promoting healthy habits, like nutrition and exercise, play a crucial role.
By addressing these factors, adolescents can lead healthier lives while receiving necessary treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Antipsychotic medications can cause weight gain in adolescents.
- Monitoring and lifestyle changes are important for managing weight.
- Early intervention can improve overall health outcomes.
Overview of Antipsychotic Drugs
Antipsychotic drugs are essential for treating certain mental health disorders. They help manage symptoms and improve quality of life for many individuals. This section explores the types of antipsychotics, their common uses, and how they work in the brain.
Types of Antipsychotics
There are two main types of antipsychotics: typical and atypical. Typical antipsychotics, also known as first-generation antipsychotics, include drugs like haloperidol and chlorpromazine. These medications primarily help reduce symptoms of psychosis, such as hallucinations and delusions.
Atypical antipsychotics, or second-generation antipsychotics, include medications like risperidone, aripiprazole, and quetiapine. These drugs are generally preferred due to their broader range of effects and typically lower risk of certain side effects. Both types have specific uses in treating various mental health conditions.
Common Uses for Antipsychotics
Antipsychotic drugs are primarily used to treat schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. They are also prescribed for severe depression, anxiety disorders, and conditions like autism spectrum disorder.
In children and adolescents, these medications can help manage aggressive behavior and mood swings. While effective, antipsychotics require careful monitoring due to potential side effects, including weight gain and metabolic issues.
How Antipsychotics Work
Antipsychotic drugs work by affecting neurotransmitters in the brain, particularly dopamine and serotonin. Many antipsychotics block dopamine receptors, which help reduce symptoms of psychosis. This action can stabilize mood and improve overall mental health.
Atypical antipsychotics often block both dopamine and serotonin receptors. This dual-action mechanism can improve symptoms while minimizing some side effects associated with typical antipsychotics. Understanding how these drugs work is vital for optimal treatment outcomes.
Understanding Weight Gain in Adolescence
Adolescents experience significant physical changes as they grow. These changes can have an impact on body weight and composition. Various factors contribute to weight gain during this stage, particularly when certain medications are involved.
Normal Adolescent Growth Patterns
During adolescence, growth patterns vary widely among individuals. Most young people undergo growth spurts, often gaining weight as they develop.
Boys: Generally, gain muscle mass and experience increased appetite and physical activity.
Girls: Often gain fat during later stages of puberty as part of normal body changes.
Weight gain in adolescence can include both fat and muscle. It’s important for parents and caregivers to recognize these changes as part of healthy development.
Factors Contributing to Weight Gain
Several factors can influence weight gain in adolescents. These may include:
Nutrition: Diets high in sugar and fats can lead to more weight gain.
Physical Activity: Many teens are less active due to increased screen time.
Medication Effects: Some medications, like antipsychotics, are linked to increased appetite and weight gain.
Mental health issues can also contribute to changes in behavior and lifestyle, making it crucial to monitor weight and health during treatment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the impact of antipsychotic medications on weight gain in adolescents is essential for promoting healthier outcomes. By implementing monitoring strategies and lifestyle changes, we can help young individuals navigate these challenges while receiving the care they need.
If you are a parent or guardian of an adolescent on antipsychotic medication, consider enrolling in our ongoing clinical trial study On weight gain in adolescents on antipsychotics at Om Research in California. Your involvement can contribute to vital research that aims to improve health outcomes for young people. Please reach out to us for more information on how to participate today!