Digestive health is the cornerstone of our overall health, which is deeply affected by lifestyle and dietary options.
Amidst general digestive issues that encounter many individuals, acid reflux stands out as a prevalent concern.
This condition occurs when the stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing discomfort and potential long-term complications.
If left untreated, acid reflux can progress into more severe conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and Erosive Esophagitis (EE).
Understanding how diet and lifestyle factors contribute to acid reflux is necessary for prevention and management.
In this blog, we will detect the significant impact of these options on esophageal health and provide strategies to promote digestive wellness.
How Diet Affects Acid Reflux and Esophageal Health
How Diet Affects Acid Reflux and Esophageal Health
Trigger Foods:
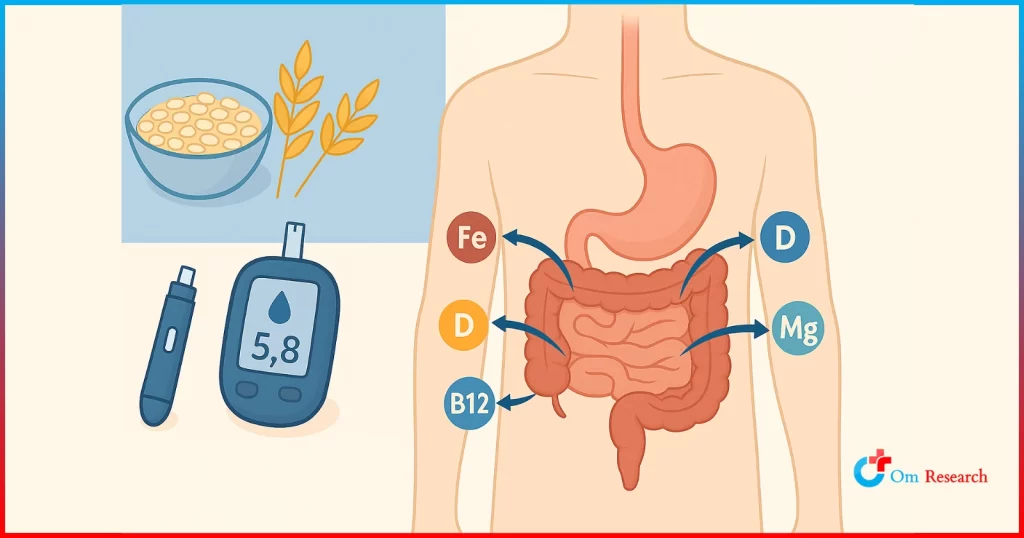
Diet plays an important role in the occurrence and severity of symptoms. Some foods may trigger reflux by relaxing the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), which prevents abdominal acid from entering the esophagus.
General trigger foods include:
- Spicy Foods: ingredients such as chili and hot sauce can disturb the esophagus.
- Fatty Food: High -fat foods, including fried foods and creamy sauce, can increase acid production.
- Caffeine and Alcohol: These relax the LES, allowing acid to flow back into the esophagus.
- Citrus Fruit: Fruit like lemons, oranges and grapes have high acidity, and they can worsen symptoms.
- Chocolate and Mint: These foods can also relax the laces, which increases the chances of reflux.
Best Food for Acid Reflux:
In contrast, some foods may help reduce acid reflux symptoms and promote esophageal health. This includes:
- Oatmeal: A nutritious, non-acidic snack option that helps to absorb stomach acid.
- Bananas: Naturally alkaline, bananas can neutralize acidity and calm the stomach.
- Leafy Greens: Vegetables like spinach and bail are high in fiber and can help prevent acid buildups.
- Non-Citrus Fruits: Apples, pears, and melons are soft on the stomach and are safe for people with this condition.
- Lean Protein: Skinless poultry, fish and plant-based proteins provide essential nutrients without excessive fat.
Lifestyle Factors That Worsen Acid Reflux
In addition to dietary effects, many lifestyle factors can increase acid reflux symptoms. Identifying and modifying these habits can lead to significant improvement in digestive health.
Obesity
The extra weight can put pressure on the stomach, pushing food in the stomach back into the esophagus. This increased abdominal pressure is an important contributor to acid reflux. In addition, bad postures, especially while sitting or lying down, can facilitate the backflow of stomach acid.
Smoking and Alcohol Consumption
Smoking is harmful to esophageal health, as it weakens the lower esophageal sphincter (LES)- a ring of muscle that forms a valve at the lower end of the esophagus- where it joins the stomach and increases stomach acid production.
Similarly, alcohol consumption relaxes LES and can worsen the symptoms of the reflux. Quitting smoking and consuming alcohol can benefit people suffering from acid reflux.
Late Night Meal
Timing food is important in the management of acid reflux. Eating large meals or snacks at bedtime can increase acid production and discomfort while lying down. It is appropriate to finish the food at least three hours before going to bed to allow the stomach to be emptied properly.
Medical Conditions Linked to Chronic Acid Reflux
Severe medical conditions can rise, if not addressed, to chronic acid reflux. Various complications can result from the ongoing performance of the esophagus for stomach acid:
GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease):
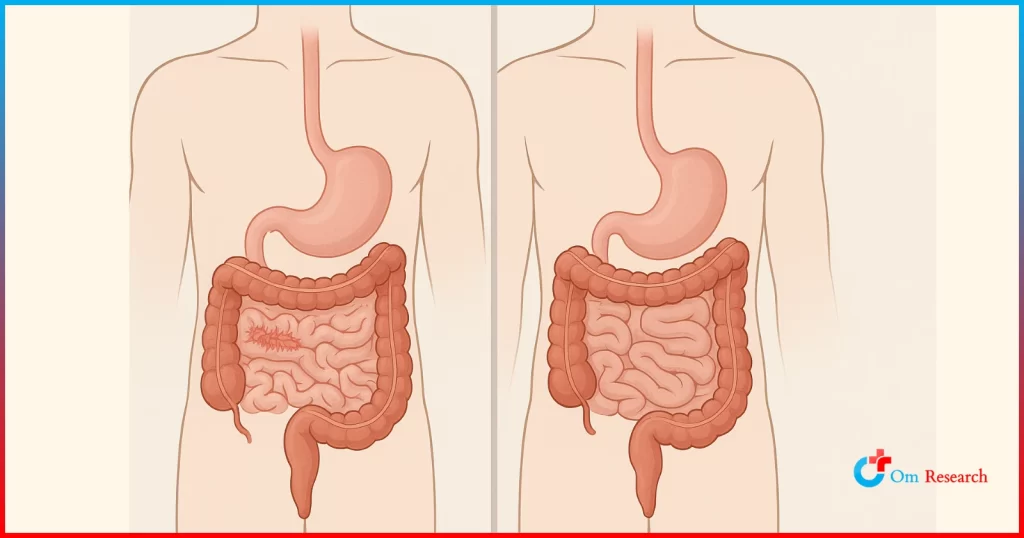
GERD is a more severe form of acid reflux characterized by persistent symptoms that can interfere with daily life. This occurs when acid reflux is more than twice a week. If untreated, GERD can cause significant damage to the esophagus and give rise to complications such as esophageal strikers and Barrett’s esophagus.
Hiatal Hernia:
This condition arises when part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity. Hiatal hernias can increase the likelihood of acid reflux, allowing stomach acid to flow more easily into the esophagus.
Erosive esophagitis occurs when the esophagus is inflamed and damaged due to prolonged contact of stomach acid. Symptoms may include painful swallowing, chest pain and potential bleeding.
Treatment & Prevention Strategies
A comprehensive approach is required to manage acid reflux, including dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, and medical intervention.
Dietary Adjustment:
It is necessary to identify and eliminate trigger foods to prevent acid reflux. Including more esophageal-friendly foods in your diet can promote digestive health. Pay attention to consuming small, more frequent food that includes fiber, lean protein and healthy fat balance. This approach helps manage stomach acid production and prevents more food.
Lifestyle Modification:
Including regular physical activity can help maintain a healthy weight and improve posture. Both are important to prevent acid reflux. Indulging in moderate exercise can also help reduce stress, which is a known trigger for acid reflux symptoms. Additionally, quitting smoking and alcohol consumption are important steps to improve esophageal health.
Medications:
For individuals experiencing more severe acids or GERDs, various drugs can help manage symptoms. H2 blockers, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), and antacids are usually helpful to reduce stomach acid production and protect the esophagus. These drugs can offer relief and promote the treatment of the esophageal lining.
Conclusion
Understanding the effect of diet and lifestyle options on acid reflux is necessary to maintain esophageal health.
By making small adjustments in your diet, such as avoiding trigger foods and involving more nutritious options, as well as adopting healthy lifestyle habits, you can greatly improve your digestive well.
If you experience chronic acid reflux, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to detect proper treatment options and protect your esophagus from prolonged damage.
Remember, the option you make today can give rise to a healthy digestive system tomorrow.