Erosive Esophagitis (EE) is a condition where the lining of the esophagus becomes inflamed and damaged due to stomach acid and other digestive juices flowing back into the esophagus.
This condition can cause symptoms such as chest pain, difficulty swallowing, and regurgitation.
Erosive Esophagitis can be caused by several factors, including refluxed stomach acid, heartburn, Excessive vomiting, Pills getting stuck, Infections, radiation injury, Injury from chemicals, hiatal hernia, and certain medications.
Clinical trials and research play a crucial role in understanding Erosive Esophagitis and developing effective treatment guidelines.
These clinical research trials help researchers evaluate the safety and efficacy of various treatments for Erosive Esophagitis, including proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), potassium channel blockers (P-Cabs), H2 blockers, and antacids.
They also help identify potential side effects associated with these treatments and determine the optimal dosage and duration of treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Clinical trials and research are essential for understanding and treating Erosive Esophagitis.
- These clinical research trials help evaluate the safety and efficacy of various treatments for Erosive Esophagitis (EE), including proton pump inhibitors, H2 blockers, and antacids.
- They also help identify potential side effects associated with these treatments and determine the optimal dosage and duration of treatment.
What is Erosive Esophagitis?
Definition and Overview of Erosive Esophagitis
Erosive Esophagitis is a condition in which the lining of the esophagus becomes inflamed and damaged due to stomach acid backing up into the esophagus.
This condition is a type of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and can cause discomfort and pain.
What is Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)?
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), often shortened to just GERD, is a chronic digestive condition impacting millions worldwide. It occurs when stomach acid and contents flow back up into the esophagus, the tube connecting your mouth to your stomach. This upward flow can irritate the lining of the esophagus, leading to a range of uncomfortable symptoms and potential complications.
The esophagus is the tube that connects the throat to the stomach, and when it becomes damaged, it can lead to complications such as ulcers, bleeding, and scarring.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Erosive Esophagitis
Symptoms of Erosive Esophagitis can include heartburn, difficulty swallowing, chest pain, and regurgitation of food or acid. These symptoms can be mild or severe and can occur intermittently or persistently.
Diagnosis of Erosive Esophagitis is usually made through an endoscopy, which is a procedure where a small camera is inserted into the esophagus to check for inflammation and damage.
Stages of Erosive Esophagitis
Esophageal erosion can occur in four stages, with each stage indicating the severity of the condition.
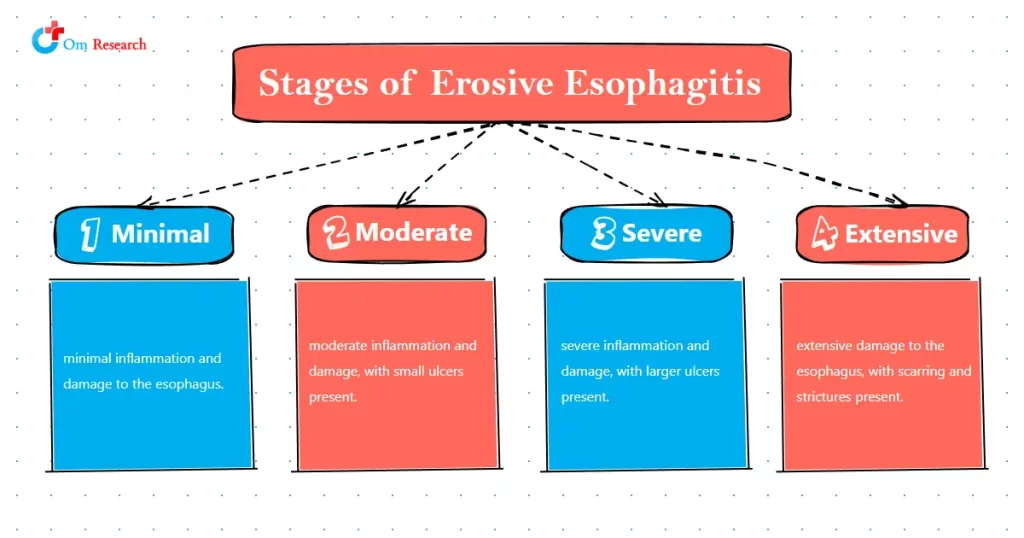
Stage 1 – Minimal Inflammation
In the first stage, there is minimal inflammation and damage to the esophagus.
Stage 2 – Moderate Inflammation and Damage
In the second stage, there is moderate inflammation and damage, with small ulcers present.
Stage 3 – Severe Inflammation and Damage
The third stage is characterized by severe inflammation and damage, with larger ulcers present.
Stage 4 – Extensive Damage To The Esophagus
In the fourth and final stage, there is extensive damage to the esophagus, with scarring and strictures present.
Overall, understanding Erosive Esophagitis is important in properly diagnosing and treating the condition. If left untreated, it can lead to complications and a decreased quality of life.
Etiology of Erosive Esophagitis
Erosive esophagitis is a condition characterized by the inflammation of the esophagus lining due to the backward flow of stomach acid. This condition is often caused by various factors such as the following:
Common Causes of Erosive Esophagitis

Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
GERD is the most common cause of erosive esophagitis. In this condition, the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) fails to close properly, allowing stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus. This repeated exposure to stomach acid can cause irritation and inflammation of the esophagus lining.
Hiatal hernia
A hiatal hernia is a condition where a portion of the stomach protrudes into the chest through the diaphragm. This can cause the LES to become weak, leading to the backward flow of stomach acid into the esophagus.
Smoking
Smoking weakens the LES and increases the production of stomach acid, which can contribute to the development of erosive esophagitis.
Alcohol consumption
Alcohol can relax the LES, allowing stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus.
Obesity
Being overweight or obese can increase the pressure on the stomach, causing the LES to weaken and leading to the backward flow of stomach acid.
Medications
Certain medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), aspirin, and bisphosphonates can irritate the esophagus lining and contribute to the development of erosive esophagitis.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy can increase the pressure on the stomach, causing the LES to weaken and leading to the backward flow of stomach acid.
In conclusion, erosive esophagitis can be caused by various factors such as GERD, hiatal hernia, smoking, alcohol consumption, obesity, medications, and pregnancy.
It is important to identify and manage the underlying cause of erosive esophagitis to prevent complications and improve quality of life.
Erosive Esophagitis Clinical Trials and Research in Camarillo
Erosive Esophagitis Clinical Trials
Erosive Esophagitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the esophagus due to chronic exposure to gastric acid.
Clinical trials are essential to evaluate the effectiveness of treatments for Erosive Esophagitis.
These trials involve the use of medications such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and potassium-competitive acid blockers (P-CABs) to relieve symptoms and promote healing of the esophagus.
Several clinical trials have been conducted to evaluate the efficacy and safety of these medications.
Erosive Esophagitis Om Research Clinical Trials in Camarillo
Om Research is a clinical research organization that conducts clinical trials to evaluate new treatments for Erosive Esophagitis.
We have conducted several clinical trials to evaluate the efficacy and safety of new medications.
In conclusion, clinical trials are essential to evaluate the effectiveness of treatments for Erosive Esophagitis. Om Research has conducted several clinical trials to evaluate the efficacy and safety of new medications.