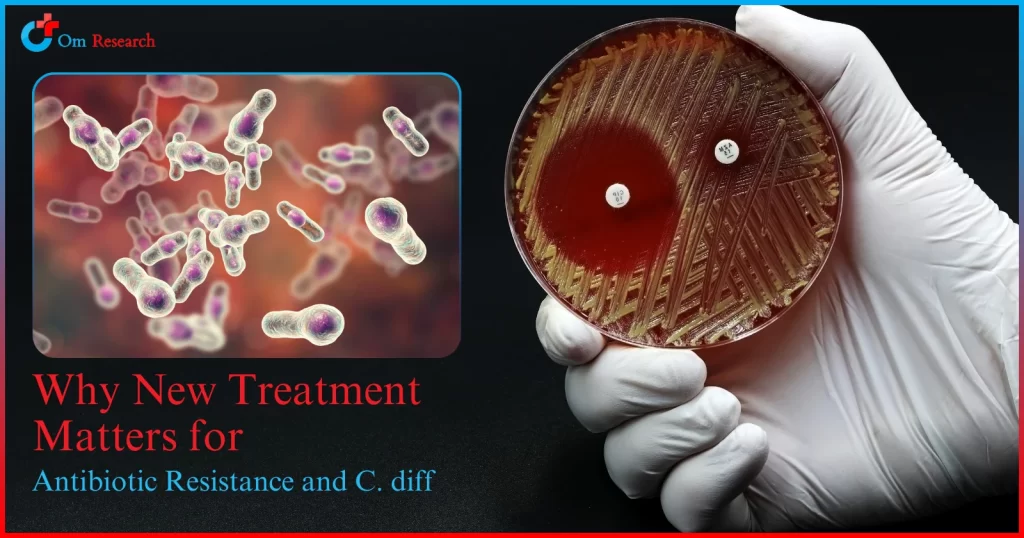
Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) is a serious bacterial infection that affects the digestive system. It’s become increasingly concerning due to antibiotic resistance, making treatment less effective.
Understanding Antibiotic Resistance in C. diff
Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria evolve to withstand the drugs designed to kill them. For C. diff, this resistance has made traditional treatments like metronidazole and vancomycin less effective in some cases. The bacteria can develop resistance through genetic mutations that allow them to survive antibiotic exposure.
The Impact on Treatment Options
When antibiotics fail, patients face longer illnesses and higher risks of complications. Recurrent clostridioides difficile, infections affect over 20% of patients, with many experiencing multiple episodes. This cycle of infection and treatment failure highlights the urgent need for alternative approaches.
Promising New Treatments
Research is advancing on several fronts:
- Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT): This procedure restores healthy gut bacteria and has shown remarkable success rates for recurrent C. diff infections.
- New Antibiotics: Drugs like fidaxomicin target C. diff while preserving beneficial gut bacteria.
- Immunotherapies: These treatments boost the body’s natural defenses against infection.
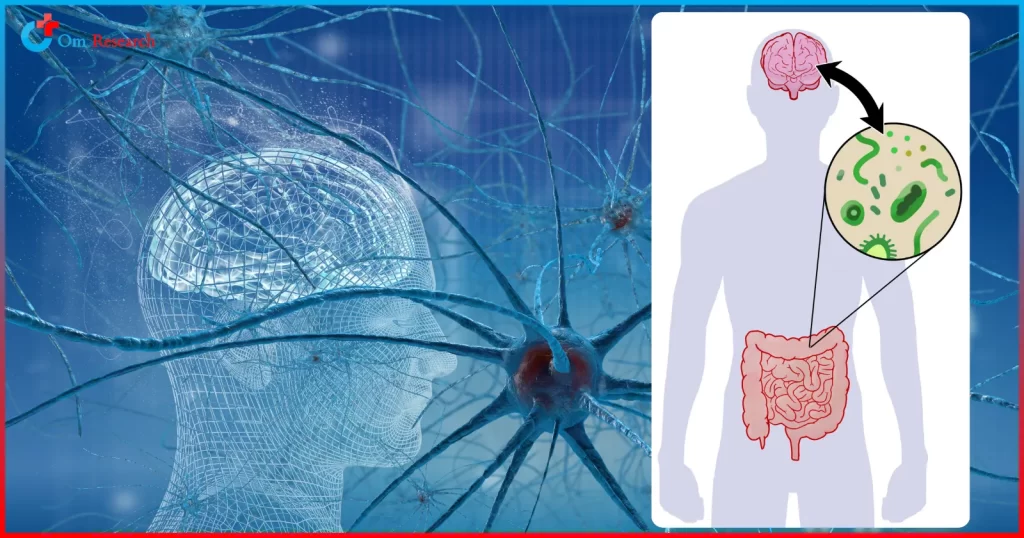
Connection to Liver Health
The gut-liver axis demonstrates how gut health impacts liver function. C. diff infections and antibiotic use can disrupt this balance, potentially leading to liver complications. Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome through effective C. diff treatment supports overall liver health.
The Role of Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are essential for developing and testing these new treatments. By participating in clinical research studies, patients can access cutting-edge therapies while contributing to medical advancement.
Conclusion
Antibiotic resistance in C. diff presents significant challenges, but innovative treatments offer hope. Continued research and participation in clinical trials will help us overcome these challenges and improve outcomes for patients.