Type II Diabetes is an increasingly common condition in the United States.
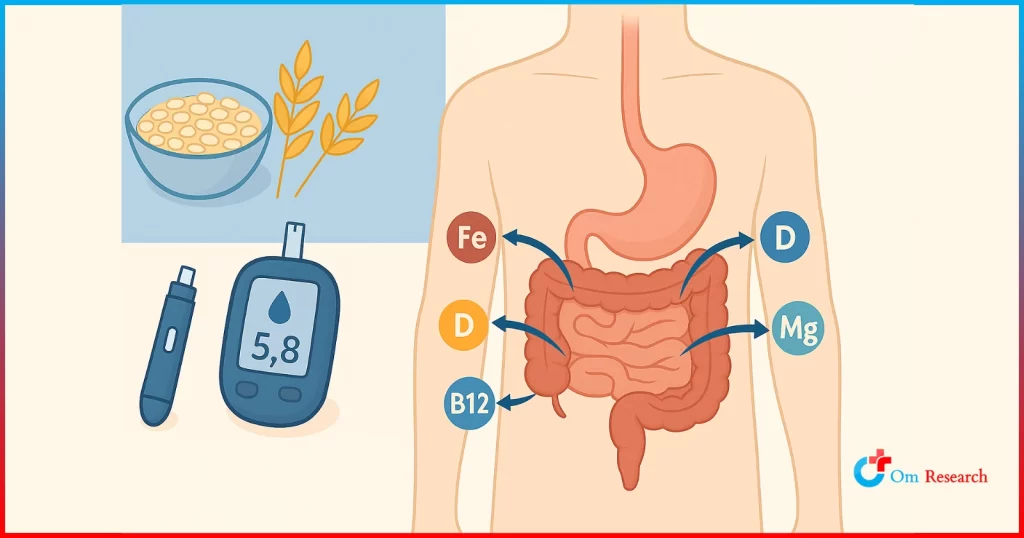
A person becomes diabetic when their pancreas can no longer produce enough insulin to process sugar, leading to high blood glucose. Managing type II diabetes is done through medication, diet changes, and exercising. Those with type II diabetes are more likely to present with obesity, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol due to their diet and exercise habits.
If someone’s diabetes progresses, it can also lead to other complications like kidney disease, fatty liver disease, ketoacidosis, neuropathy and gastroparesis.
What Health Problems Can People with Diabetes Develop?
Following a good diabetes care plan can help prevent many diabetes-related health problems. However, if it is not controlled, diabetes may cause:
- heart disease and stroke
- nerve damage
- kidney disease
- foot problems
- eye disease
- gum disease and other dental problems
- sexual and bladder problems
Many people with type 2 diabetes also have MAFLD. You can improve MAFLD by losing weight if you are overweight or have obesity. Type 2 diabetes also is connected to other health problems such as sleep apnea, depression, some types of cancer, and dementia.
What are the Causes of Type 2 Diabetes
- overweight and obesity
- not being physically active
- insulin resistance
- genes
What are the Symptoms for Type 2 Diabetes?
Symptoms of diabetes include
- increased thirst and urination
- increased hunger
- feeling tired
- blurred vision
- numbness or tingling in the feet or hands
- sores that do not heal
- unexplained weight loss
Type 2 diabetes symptoms often develop over several years and can be very mild that you might not notice them. Many people have no symptoms at all. Some people do not find out they have the disease until they have diabetes-related health problems, such as blurred vision or heart disease.
How do I manage my type 2 diabetes?
Controlling your blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol—and stopping smoking if you smoke will help manage your type 2 diabetes. Lifestyle changes, planning healthy meals, cutting down on calories if you are overweight, and being physically active are also part of managing your diabetes, so is taking any prescribed medicines for type 2 diabetes. Work with your healthcare team to create a diabetes care plan that works for you.
How Can I Prevent Type 2 Diabetes?
There are definite ways to reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes or at least delay its onset, which involve:
- Exercising regularly for at least 150 minutes (about 2 and a half hours) a week.
- Maintaining a weight that’s healthy for you.
- Eating nutritious food.
- Not smoking.
Unfortunately, some have such a high genetic risk that even lifestyle changes cannot prevent developing Type 2 Diabetes.
Living with Type 2 Diabetes
It is a convoluted condition that requires daily management, effort, and planning. Here are a few tips that can help one manage T2D:
- Try to stick to healthy lifestyle changes: This plan incorporates an emphasis on regular exercise and healthy eating as key parts of managing T2D. Set small goals and focus on making one change at a time; this will help to avoid feeling overwhelmed.
- Check your blood sugar regularly: Blood glucose monitoring is one of the critical components of diabetes management that helps one avoid its complications. Check your blood sugar with a fingerstick and meter and/or continuous glucose monitor (CGM) as often as recommended by your provider.
- Take your medication regularly: Follow your provider’s instructions for taking your medications if you have them.
- See your diabetes provider regularly: It is important to see the provider helping you manage your T2D regularly. This is to ensure that your management plan is working. Don’t be afraid to ask specific questions about them.
- See your other healthcare providers regularly, especially your eye doctor: Sometimes, type 2 diabetes can cause complications in all parts of your body, especially in your eyes. Be sure to see your eye doctor at least once a year so that he or she can check the health of your eyes.
- Have a sick day plan: Discuss how to take good care of yourself and manage T2D when you’re sick with your diabetes provider. Being sick can make it harder to control your blood sugar levels, and you may risk developing HHS.
- Stay educated: Do not hesitate to ask your provider whatever there is on your mind about type 2 diabetes. The more you become knowledgeable about T2D and its management, the more you’ll be able to lead a healthy and complications-free life.
- Find community: Connecting with others who have T2D may decrease feelings of isolation, whether that connection is made in person or online.
- Take care of your mental health: Diabetes sufferers have a two to three times higher chance of experiencing depression and a 20% higher likelihood of receiving an anxiety diagnosis compared to those without diabetes. Dealing with a long-term health issue that needs ongoing attention can be too much to handle. Remember to reach out to a mental health expert if you notice signs of depression or anxiety.
Conclusion
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and potential complications of type 2 diabetes is crucial for effective management and prevention of further health issues. By staying informed, adhering to a personalized diabetes care plan, and seeking support from healthcare professionals and communities, individuals with Type 2 diabetes can lead healthy and fulfilling lives. Remember, small, consistent efforts in managing your health can make a significant difference in your overall well-being.
Type 2 Diabetes Clinical Trials
We’re conducting studies for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH) Study; a condition type II diabetics are at a higher risk for.
If you would like more information, or would like to participate, please contact us.